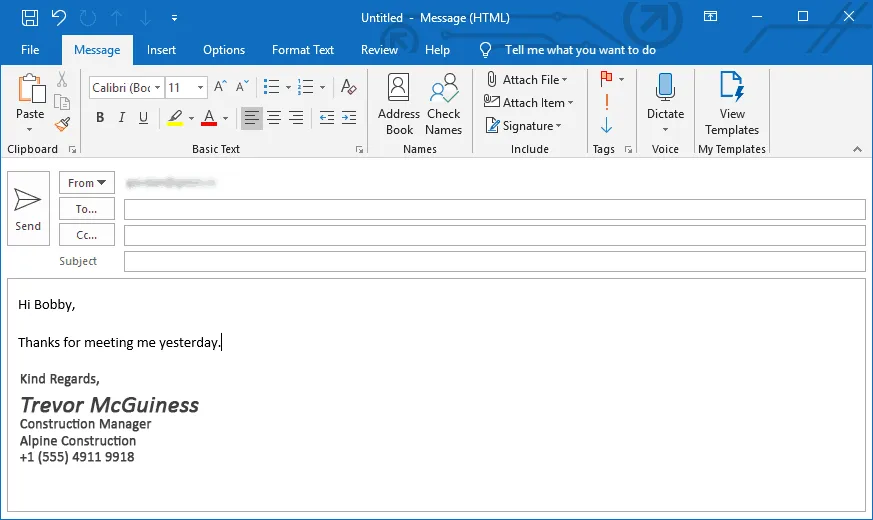
With iOS 5, Apple did add a limited rich text formatting capability. You can see it in action in the Mail app, where you can select among bold, italics, and underlined text when composing a message. In the Mail app on your Mac, in a new message window, click the Format button in the toolbar (or use the Touch Bar). Click the button for an option you want to.
- Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Address
- Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail
- Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Free
- Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Merge
In the Format and account section of the dialog box, check or uncheck Compose messages in HTML by default. Close the dialog box. Change the Setting for One Message You can also switch between HTML or plain text for an individual message: while composing a message, click the Options tab, then toggle the Format control. What version of Mail.app are you. Composing tab and choose to send 'Rich Text' mail. Text from MS Word to Mac Mail does not preserve formatting. When you reply to a message, Outlook preserves the format of the original message. If you select the Read all standard mail in plain text option, however, Outlook formats your reply in plain text. Or you can click the InfoBar, change the format of the message to HTML or Rich Text, and then reply.If you change the format of the message, the reply is formatted with the new display format.
Mail User Guide
There are a variety of ways to enter or work with text, characters, and symbols when you write a new message.
Change fonts and styles
In the Mail app on your Mac, in a new message window, click the Format button in the toolbar (or use the Touch Bar).
Click the button for an option you want to use.
More formatting options are available in the Format menu in the menu bar.
You can set the fonts you prefer to use in Mail all the time. Choose Mail > Preferences, then click Fonts & Colors. To learn about each option, click the Help button in the pane.
Copy and paste text
In the Mail app on your Mac, do any of the following:
Copy all the text in a message: Put the pointer anywhere in the message body (where the text of the message is), choose Edit > Select All, then choose Edit > Copy.
Paste text: Choose Edit > Paste.
Paste text using the surrounding style: Choose Edit > Paste and Match Style.
Paste text as a quotation: Choose Edit > Paste as Quotation. A vertical bar appears next to the text you pasted.
Include web links
In the Mail app on your Mac, do any of the following:
Enter a URL—such as apple.com—or paste a URL into your message. Mail automatically turns it into a link.
Select the text in your message that you want to turn into a link, choose Edit > Add Link, then type a URL for the link.
From the Safari address bar, drag a web address into your message. You can also email the webpage from Safari.
Include characters and symbols
In the Mail app on your Mac, do any of the following in a new message window:
Click the Emoji button in the toolbar or choose Edit > Emoji & Symbols.
You can use the Character Viewer to add emoticons or symbols, and type characters in different languages, such as Arabic or Japanese. See Use emoji and symbols.
Type accent marks or diacritical marks. See Enter characters with accent marks.
Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Address
You can set a system preference to automatically replace text or characters as you type in Mail. For example, if you type “teh,” it’s automatically replaced with “the.” See Replace text and punctuation in documents.
You can see suggested spellings for words, add frequently used words or terms to a dictionary, or choose dictionaries for specific languages. See Check spelling and grammar.
There are settings in Outlook, Outlook on the web, and Exchange Online that control the format of email messages and how they are sent to people on other domains. The default settings work in most cases. If specific recipients have trouble reading messages sent from your organization, you can adjust the settings for individual users, or for all users on a specific domain. For example, you can prevent recipients from receiving a winmail.dat attachment.
There are two types of settings you can use:
Message format: When a user creates a message, they can choose the message format in which to author the message. In Outlook, they have a choice between plain text, HTML, and rich-text format. In Outlook on the web (formerly known as Outlook Web App) they have a choice between plain text and HTML.
Message transmission: This means how the message is actually sent to the other email system. Exchange can send messages to other domains by using Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) or Transport Neutral Encapsulation Format (TNEF). All three message formats can be sent using TNEF. Only HTML and plain text can be sent using MIME. Message transmission format can be set by an admin per domain or per recipient, and users can also specify message transmission format.
Message formats
The following list describes the three message formats available in Exchange Online, and shows which ones are available in Outlook and Outlook on the web:
Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail
| Format | Description | Available in Outlook | Available in Outlook on the web |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain text | A plain text message uses only US-ASCII text as described in RFC 2822. The message can't contain different fonts or other text formatting. | Yes | Yes |
| HTML | An HTML message supports text formatting, background images, tables, bullet points, and other graphical elements. | Yes | Yes |
| Rich text format (RTF) | RTF supports text formatting and other graphical elements. Only Outlook, Outlook on the web, and a few other MAPI email clients understand RTF messages. | Yes | Can read messages formatted in RTF, but can't format or send this format |
Message transmission formats for mail sent to external recipients
The following table describes the message transmission formats that Exchange Online uses to send email messages to external recipients.
| Transmission format | Description |
|---|---|
| Transport Neutral Encapsulation Format (TNEF) | TNEF is a Microsoft-specific format for transmitting formatted email messages. A TNEF message contains a plain text version of the message and an attachment that packages the original formatted version of the message. Typically, this attachment is named Winmail.dat. The Winmail.dat attachment includes formatting, attachments, and Outlook-specific features such as meeting requests. An email client that fully understands TNEF, such as Outlook, processes the Winmail.dat attachment and displays the original message content without ever displaying the Winmail.dat attachment. An email client that doesn't understand TNEF may present a TNEF message in any of the following ways: The plain text version of the message is displayed, and the message contains an attachment named Winmail.dat, Win.dat, or some other generic name such as Att_nnnnn_.dat or Att_nnnnn_.eml where the nnnnn placeholder represents a random number. The plain text version of the message is displayed. The TNEF attachment is ignored or removed. The result is a plain text message. There are third-party utilities that can help convert Winmail.dat attachments. |
| Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) | MIME is an internet standard that supports text in character sets other than ASCII, non-text attachments, message bodies with multiple parts, and header information in non-ASCII character sets. |
Message format and transmission settings
Admins and users can control message formatting and transmission. Admin settings override user settings.
Admins can control the following settings:
Remote domain settings: Remote domain settings control the format of messages sent to people on the remote domain. You can control the format for a specific external domain, or for all external domains. For more information about remote domains, see Remote domains in Exchange Online. The remote domain settings override the per-user settings set by admins or users.
Mail user and mail contact settings: You can change settings for individual recipients by changing settings for specific mail users or mail contacts. Mail users and mail contacts are similar because both have external email addresses and contain information about people outside the Exchange Online organization. The main difference is mail users have user IDs that can be used to sign in to the Exchange Online organization. When an admin changes a per-recipient setting, it overrides settings that a user sets for that recipient. For more information about the admin settings, see Manage mail users and Manage mail contacts.
Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Free
Users can control the following settings:
Apps For Formatting Rich Text Newsletters For Mac Mail Merge
Outlook settings: In Outlook, you can set the message formatting and encoding options described in the following list:
Message format: You can set the default message format for all messages. You can override the default message format as you compose a specific message.
Internet message format: You can control whether TNEF messages are sent to remote recipients or whether they are first converted to a more compatible format. You can also specify various message encoding options for messages sent to remote recipients. These settings don't apply to messages sent to recipients in the Exchange Online organization.
Internet recipient message format: You can control whether TNEF messages are sent to specific recipients or whether they are first converted to a more compatible format. You can set the options for specific contacts in your Contacts folder, and you can override these options for a specific recipient in the To, Cc, or Bcc fields as you compose a message. These options aren't available for recipients in the Exchange Online organization.
Internet recipient message encoding options: You can control the MIME or plain text encoding options for specific contacts in your Contacts folder, and you can override these options for a specific recipient in the To, Cc, or Bcc fields as you compose a message. These options aren't available for recipients in the Exchange Online organization.
International options: You can control the character sets used in messages.
For more information about Outlook settings, see Change the message format in Outlook.
Outlook on the web settings: You can set the default message format for all messages. You can override the default message format as you compose a specific message.

Comments are closed.